1. About pysdg
Python Synthetic Data Generator (pysdg) is a package designed by the Electronic Health Information Laboratory (EHIL) at the CHEO Research Institute. The package is used to streamline the generation of synthetic data for clinical trials and support various types of analyses. It ensures consistency and robustness when handling different tabular datasets and generative models. The package acts as a wrapper for several reliable generative modeling implementations.
The package generates single or multiple synthetic datasets (synths) from the input raw tabular csv dataset. The basic description of the real raw dataset can be optionally provided as a json file. In the json file, the user defines the indices of the categorical variables, continuous variables and others. To generate the required number of synthetic versions (i.e. synths), the user can use any of the available generators listed in Usage. Please note that the replica_seq generator is developed by Aetion Generate and requires proper license and credentials to be defined by the user in a separate .env file. However, pysdg can be used without the replica_seq generator.
The following section illustrates pysdg core module to train models and generate synthetic data. We introduce the concepts of raw, real and synth datasets.
For any queries, please contact Samer El Kababji (skababji@ehealthinformation.ca)
1.1. Core functionality
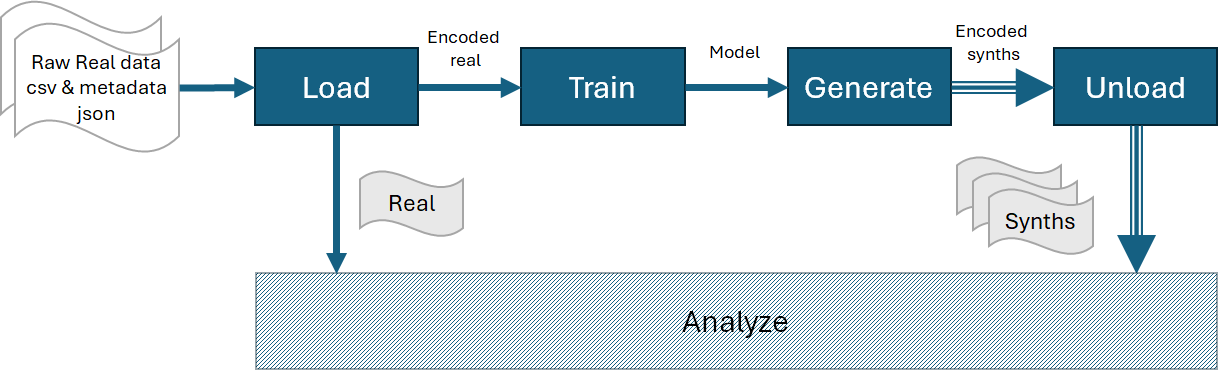
pysdg includes the essential modules to carry out the functions illustrated by the dark background blocks in the above diagram. To generate one or multiple synthetic datasets (aka synthetic dataset versions), follow these steps in sequence: Load, Train, Generate, and Unload. The raw tabular dataset is loaded as a csv file or pandas dataframe. In addition, the dataset’s user-defined metadata is optionally loaded as a json file. Please refer to Usage for the details of various keys in the json file. In return, the user gets the real dataset which is a clean version of the raw dataset. The real dataset can be used for direct comparison with the synthetic datasets. The load function also encodes the input raw data in a consistent manner and independent from the reading library. The encoded data is then used to train a selected generative model. Once trained, any required number of records and synthetic dataset versions are sampled form the generative model. The models can be saved for future sampling. The list of generated synthetic datasets are referred to as synths.